Editor’s Note: The following article is derived from officially released information, published with few or no editorial changes. The Greylock Glass occasionally provides our readers with such content if the information is factual in nature, and requires little to no interpretation or analysis, often when original reportage would provide little to no additional relevant information.
BOSTON — Opioid-related overdose deaths in Massachusetts rose slightly in the first nine months of 2021 compared to the same time last year, according to preliminary data released today by the Massachusetts Department of Public Health (DPH). In the first nine months of the year, there were 1,613 confirmed and estimated opioid-related overdose deaths, approximately 21 more deaths than in the first nine months of 2020, or a 1 percent increase. Data released earlier this year noted that Black non-Hispanic men made up the largest increase in opioid overdose death rates, a finding reinforced by today’s report, and which underscores the importance of the Commonwealth’s continued investments to address this issue with a focus on equity.
Throughout the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and related public health challenges, the Commonwealth has continued to focus on the opioid epidemic, most recently investing over $45 million in federal dollars to support prevention, treatment, and recovery programs for vulnerable populations. This includes a combined $19 million for early childhood and youth substance use prevention, treatment, and recovery programs; $9 million for low-threshold access to treatment for people struggling with opioid use disorder; $2.8 million for treatment for people experiencing homelessness; and a combined $11.3 million to support transitional and permanent housing programs for adults, families, and young adults in treatment and recovery from substance abuse disorder.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated substance misuse not only in Massachusetts, but across the country. Our Administration has continued to tackle both the opioid epidemic and the COVID-19 pandemic with a focus on equity,” said Governor Charlie Baker. “Since 2015, we have more than doubled spending on substance misuse programs across state government, boosted the number of treatment beds, and signed two landmark laws to respond to this public health crisis. We continue to invest in treatment, support, intervention, and education programs, primarily for residents experiencing the highest burden of this epidemic.”
“We remain committed to increasing resources to battle the opioid crisis amid the challenges presented by the COVID-19 pandemic over the past 20 months, particularly for those struggling with substance use and mental health disorders,” said Lt. Governor Karyn Polito. “We will continue to work collaboratively with all stakeholders to ensure residents struggling with addiction have access to necessary supports.”
We have seen the impacts of the intersecting COVID-19 pandemic and opioid epidemic on some of our most vulnerable communities.
Health and Human Services Secretary Marylou Sudders
The Baker-Polito Administration has continued to build on its work and funding to address this crisis, more than doubling investments in this area since 2015. The Fiscal Year 2022 budget includes a total investment of $408 million across various state agencies to address substance misuse, a 22 percent increase over last fiscal year, and an increase of $288.8 million (242%) since FY15.
Since the early days of the pandemic, the Administration has continued to expand overdose-targeted initiatives to ensure uninterrupted substance use treatment and support. DPH has distributed more than 124,000 naloxone kits to opioid treatment programs, community health centers, hospital emergency departments, and houses of correction since March 2020. With a blanket exception from the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), 35 percent of Massachusetts opioid treatment program patients have been receiving take-home doses of medication for opioid use disorder (MOUD) as of September 2021, compared to the pre-pandemic average of 16 percent in December 2019.
Massachusetts is among the states with the smallest increases nationwide in all drug overdose deaths between March 2020 and March 2021, according to the latest preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The data show that while drug overdose deaths surged by 31 percent nationally in that time period, Massachusetts’ increase was in the single digits.
Unfortunately, the pandemic exacerbated the opioid crisis, particularly in communities of color which have also been disproportionately impacted by COVID-19.
Acting Public Health Commissioner Margret Cooke
“We have seen the impacts of the intersecting COVID-19 pandemic and opioid epidemic on some of our most vulnerable communities,” said Health and Human Services Secretary Marylou Sudders. “As the Commonwealth emerges from the pandemic, we must engage with trusted community-based health care providers to provide culturally responsive support and treatment.”
“Prior to the pandemic, opioid-related overdose death rates in Massachusetts had been stable. Unfortunately, the pandemic exacerbated the opioid crisis, particularly in communities of color which have also been disproportionately impacted by COVID-19,” said Acting Public Health Commissioner Margret Cooke. “Our goal is to reverse this troubling trend by continuing to build on our aggressive, data- and equity-based public health approach to prevention, intervention, treatment, and recovery.”
Overall, there were 2,106 opioid-related overdose deaths in 2020, a 5 percent increase over the previous year and just shy of the 2016 peak of 2,110 deaths, according to the latest preliminary data. The 2020 opioid-related overdose death rate of 30.2 per 100,000 people was approximately 1.6 percent lower than in 2016 (30.7 per 100,000), the latest data show.
In 2021, the powerful lethal synthetic opioid fentanyl continues to be the main driver of opioid-related overdose deaths in Massachusetts. In the first half of 2021, fentanyl was present in 92 percent of opioid-related deaths where a toxicology report was available, preliminary data show.
The following cities and towns experienced a notable decrease in opioid-related overdose deaths in 2020 compared with 2019.
| Towns Experiencing a Notable Decrease in Opioid-Related Overdose Deaths from 2019 to 2020 that Meet Criteria | |||
| Town | Residence | Occurrence | Both |
| Attleboro | X | ||
| Lawrence | X | ||
| Leominster | X | ||
| Lynn | X | ||
| Northampton | X | ||
| Taunton | X | ||
| Westfield | X |
The following cities and towns experienced a notable increase in opioid-related overdose deaths in 2020 compared with 2019.
| Towns Experiencing a Notable Increase in Opioid-Related Overdose Deaths from 2019 to 2020 that Meet Criteria | |||
| Town | Residence | Occurrence | Both |
| Boston | X | ||
| Brockton | X | ||
| Holyoke | X | ||
| Malden | X | ||
| Salem | X | ||
| Springfield | X | ||
| Stoughton | X | ||
| Weymouth | X | ||
| Worcester | X |
Cocaine is the next most prevalent drug among opioid-related overdose deaths after fentanyl, present in 52 percent of toxicology reports in the first six months of 2021 – a 13 percent increase over 2020. In 2017, cocaine was present in 39 percent of opioid-related overdose deaths.
The rate of heroin or likely heroin present in opioid-related overdose deaths was 9 percent and has been declining since 2014. The presence of benzodiazepines, amphetamines, and prescription opioids in opioid-related overdose deaths remained stable in the first half of the year, toxicology screens show. The percentage of benzodiazepine has been declining since 2018.
In the first half of 2021, males ages 25-34 continued to represent the greatest number of suspected opioid-related incidents treated by Emergency Medical Services (EMS), accounting for 22 percent of opioid-related incidents with a known age and sex.
Among the other findings of the latest opioid report:
- Between 2019 and 2020, the confirmed opioid-related overdose death rate for white non-Hispanic residents decreased slightly: 33.4 per 100,000 in 2019 to 33.1 per 100,000 in 2020. Meanwhile, the rate for all Black non-Hispanic residents increased 63 percent from 22 to 36 per 100,000.
- The confirmed opioid-related overdose death rate for Asian Pacific Islander non-Hispanic residents increased about 27 percent from 2.6 to 3.3 per 100,000 between 2019 and 2020. For Hispanic residents the rate increased over 12 percent from 32 to 36 per 100,000.
- In the same time period, the confirmed opioid-related overdose death rate per 100,000 for Black non-Hispanic, Asian Pacific Islander non-Hispanic, and Hispanic men increased, while it decreased for white non-Hispanic men.
- Between 2019 and 2020, the opioid-related overdose death rate among all females increased by 15 percent, from 14 to 16 per 100,000.
- In the same time period, the confirmed opioid-related overdose death rate increased for Black non-Hispanic, Hispanic, and white non-Hispanic women:
- Black non-Hispanic up 32 percent from 12 to 16 per 100,000
- Hispanic up 68 percent from 8 to 14 per 100,000
- White non-Hispanic up 8 percent from 17 to 19 per 100,000
- Males comprise 73 percent of all opioid-related overdose deaths occurring in 2020.
- In 2020, 50 percent of opioid-related deaths occurred in people who were between 25 and 44 years old; 40 percent were between 45 and 64 years old.
- Naloxone was administered in 96 percent of acute opioid overdoses during the first six months of 2021. Of all opioid-related EMS incidents in the first half of 2021, 53.1 percent were categorized as acute opioid overdoses.
- Approximately 469,000 individuals in Massachusetts received prescriptions for Schedule II opioids in the third quarter of 2021, a 44 percent decrease from 841,990 in the first quarter of 2015.
The following cities and towns experienced a notable decrease in opioid-related overdose deaths in 2020 compared with 2019.
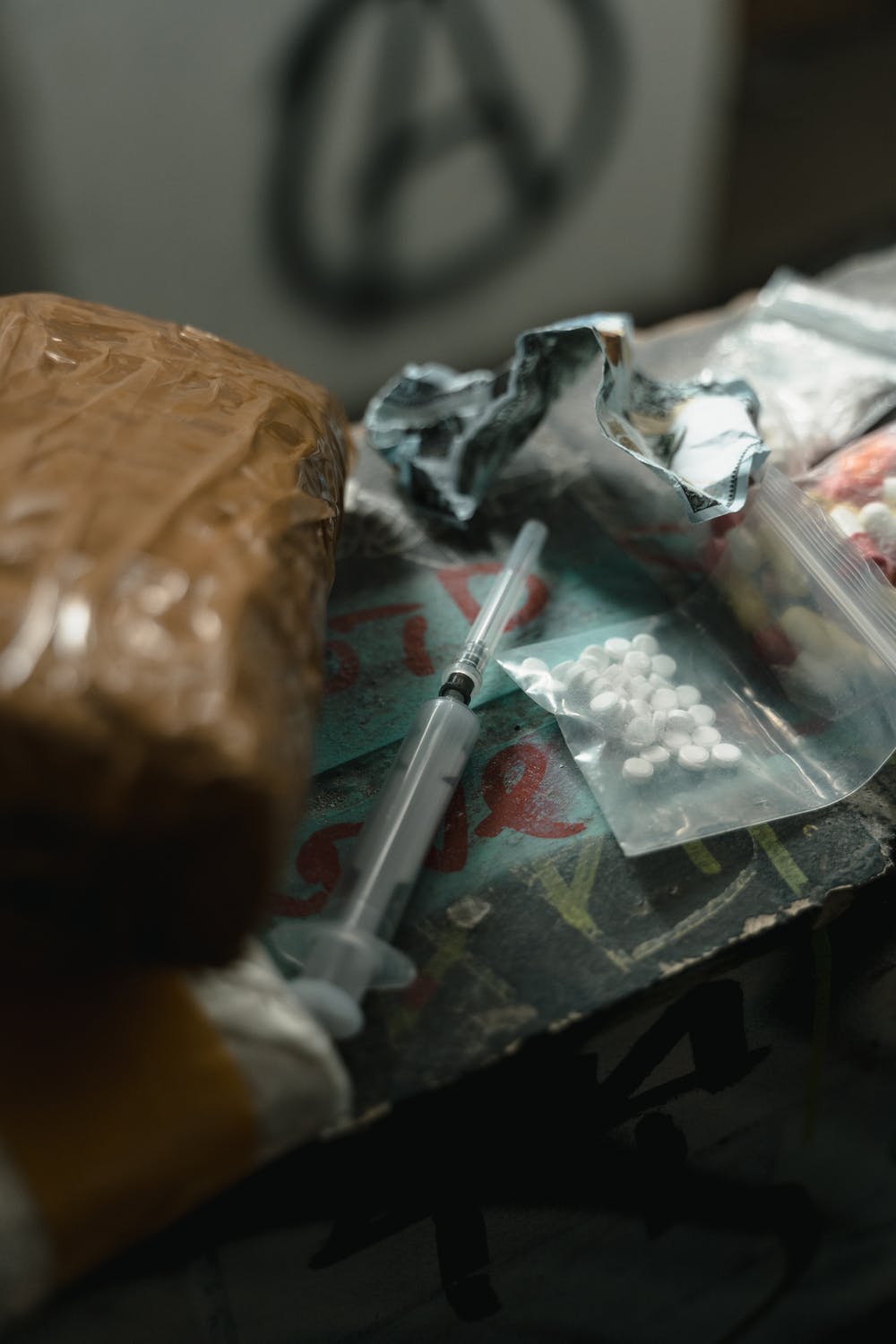

















It’s a very bad crisis and so many people are passing at young ages, and so many lives are stultified and captured by this, and it’s caused by the alienation of the system we live in crushing the human spirit on a daily basis.
Narcan saves lives. Some see it as a chance to continue to use. Others see it as a chance to never use again.
Unfortunately what drives much of substance use is abuse, neglect, economic disparity, abandonment, etc. When you look at where the support dollars go, it simply doesn’t address the realities… Of the 5 countries with the highest drug abuse rates, the U.S. sits in 4th place, behind Iran, Afghanistan, and Russia. That alone should be telling, but we don’t want to present this nation in that comparison because that destroys our global image of a successful super power. Drug trafficking supports world economies, including ours. All solutions are found at the source and ours is eternally an after thought. We play the blame game like no other, providing bandaid aftercare to appear compassionate. This is the sad reality of how we have for decades driven our image. So I’ll save my pats on the backs for a time of clear reality solutions, when the core of our nation isn’t the driving force of our addictions…