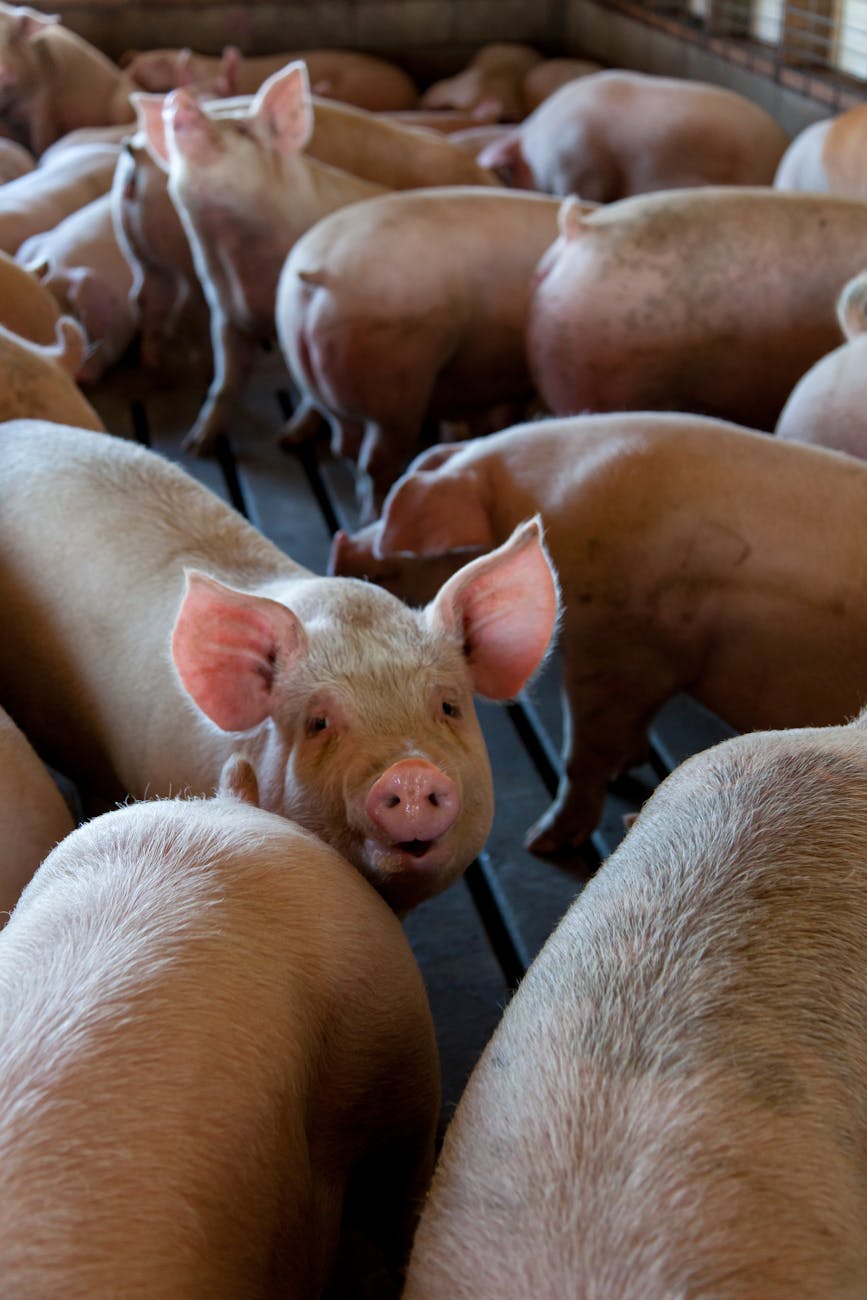
Advocates said a lack of animal welfare laws is leading to pain and suffering on American factory farms.
Close to 99% of livestock is now raised in industrial-type facilities, where animal welfare groups said efficiency and profitability take precedence over animals’ well-being.
Delcianna Winders, associate professor of law and director of the Animal Law and Policy Institute at Vermont Law and Graduate School, said while more than a dozen states have banned what are deemed torture-like confinement for animals, there is no federal law protecting them from abuse.
“If most people were aware that the animal they’re sitting down to eat couldn’t move throughout their entire life, just to give one example, I don’t think they would want to support that,” Winders contended.
Winders pointed out the Humane Methods of Slaughter Act requires animals be knocked unconscious before they are killed but corporations running factory farms are lobbying for the law to be weakened in order to speed up meat production.
So-called “ag-gag” laws in several states criminally penalize those who seek to expose animal suffering on farms, in slaughterhouses and at animal auctions. Winders added she is concerned a second Trump Administration could allow factory farm owners to further erode any remaining health and safety standards.
“They’ve been able to carve themselves out from complying with the laws that everybody else has to comply with,” Winders asserted. “That certainly includes cruelty-to-animals laws. It also includes pollution laws, worker-safety laws, the whole gamut.”
Winders advised people concerned with animal welfare to try more plant-based alternatives to meat and learn more about how their food is raised. She stressed as consumers increasingly turn to “organic” and “free-range” meat options, corporations are working to lower the standards for what those labels mean and the conditions under which those animals can be raised.
This story is based on original reporting by Seth Millstein for Sentient.